Benign Prostate Gland Enlargement (BPH)

Male Voiding Dysfunction
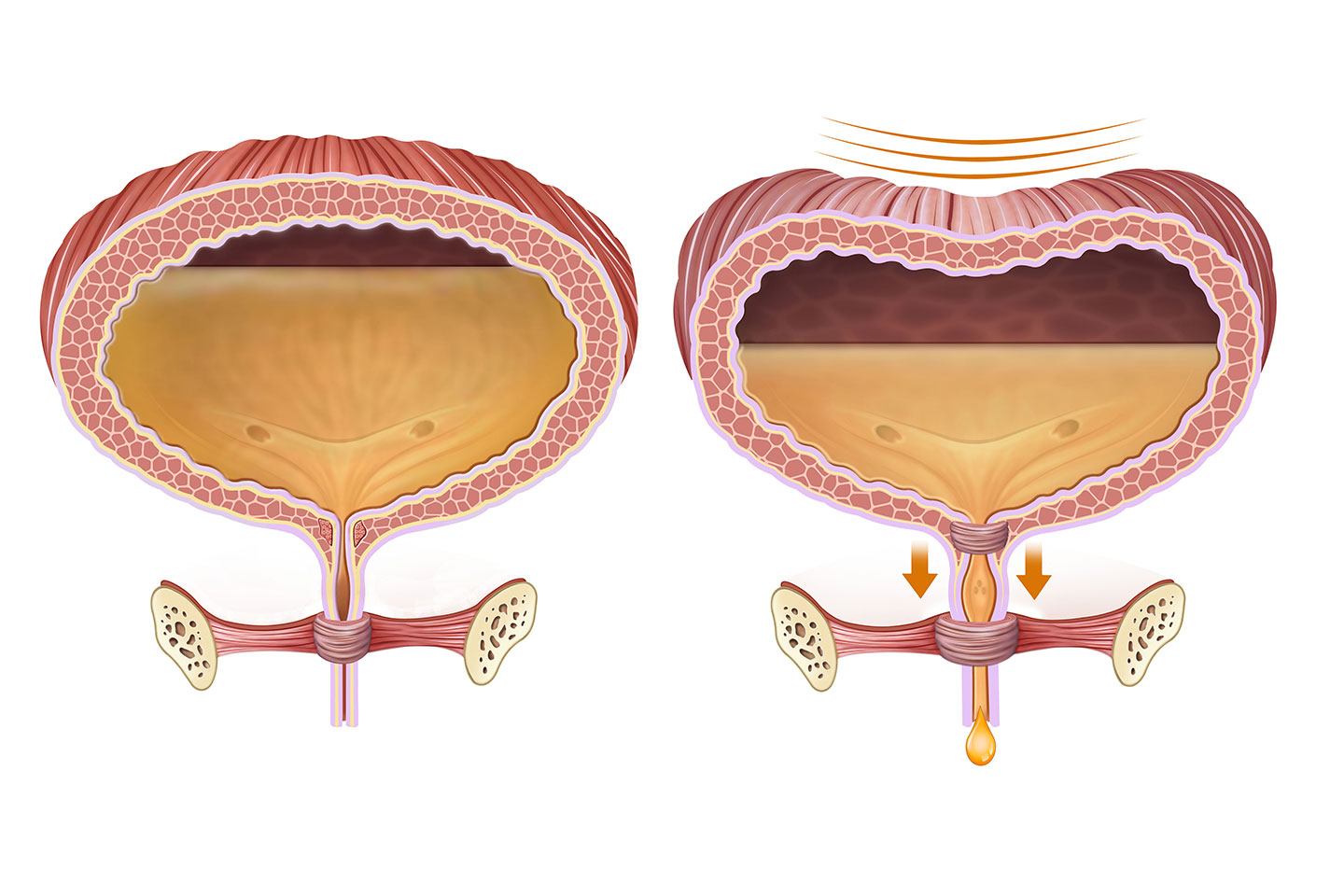
Difficulty in urination in men can occur due to numerous reasons. The symptoms can be divided into storage symptoms, where a man is unable to hold the urine for long periods of time or has developed a very small bladder capacity.
There are also emptying symptoms, where the main issue is the inability to effectively empty the bladder with symptoms of obstruction such as hesitancy, intermittent urination, dribbling, repeated trips to the bathroom to urinate due to incomplete emptying the bladder, and post void dribbling.
Male Voiding Dysfunction & Female Voiding Disfunction
The lower urinary tract in the male includes the bladder, prostate and urethra, which allows for storage and timely expulsion of urine. Voiding dysfunction describes a condition in which there is dysregulation of the natural systems which regulate voiding and may involve the bladder muscle, the prostate and the urethra. Voiding symptoms represent a continuum of what is referred to as Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS).

Kidney Stones
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a medical condition where a man is unable to achieve and maintain an erection that allows for satisfactory sexual function. This can show up in several different ways, from a less firm erection, to erections not occurring as frequently as previous times, to a complete inability to achieve erections despite normal sexual sensation.
For some men, coitus may not be possible anymore, while others may lose their erections too quickly for successful completion of intercourse. Men with ED often lose confidence in their sexual ability and their overall sense of self-worth can be negatively affected. Erectile dysfunction often has an important psychological impact on the man, and his relationship with his partner, and men don’t often seek help for this ailment out of shame.


Hematuria (Blood in Urine)
When blood is found in your urine via routine testing but your family doctor, or if you see it yourself, both situations may be serious and require investigation by a urologist. Since the source of the blood may be anywhere along the urinary tract from the kidney all the way down to the urethra, as well as involve blood conditions or conditions which themselves may negatively affect the health of the kidney, the gold standard to evaluate the entire urinary tract.
Urinary Obstruction
Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction occurs in the upper urinary. Most often, it is blocked at the renal pelvis. This is where the kidney attaches to one of the ureters (the tubes that carry urine to the bladder). The blockage slows or stops the flow of urine out of the kidney. Urine can then build up and damage the kidney. Sometime, surgery is needed to improve the flow of urine and other times the problem will improve on its own. When surgery is required, a minimally invasive reconstruction is considered to be the gold standard, although other modalities are available as well. The minimally invasive approach is called a laparoscopic pyeloplasty.The treatment always needs to be tailored to the patients needs, surgical fitness, expectations and anatomy.

Surgery, Medical Management of BPH
When blood is found in your urine via routine testing but your family doctor, or if you see it yourself, both situations may be serious and require investigation by a urologist. Since the source of the blood may be anywhere along the urinary tract from the kidney all the way down to the urethra, as well as involve blood conditions or conditions which themselves may nWhen BPH needs to be treated, the first thing that is trying is modification of Lifestyle factors. There may be food restriction past a certain time at night if your symptoms involve urinating very frequently overnight, and a withholding of caffeine and a stopping of smoking are quite effective as well. Should these Maneuvers not help the symptoms, there are pelvic floor exercises, biofeedback, as well as other lifestyle modifications that are possible. When these basic Maneuvers do not help, often medication is necessary. The following medications may be indicated:egatively affect the health of the kidney, the gold standard to evaluate the entire urinary tract.
Low Testosterone
Male hypogonadism is a condition in which the body doesn’t produce enough of the hormone that plays a key role in masculine growth and development during puberty (testosterone) or enough sperm or both. You can be born with low testosterone, or it can develop later in life due to illness, injury or infection. The effects and treatment entirely depend on your gae and how strongly the symptoms affect your daily life. If there is a constellation of symptoms present, such as sexual dysfunction, poor concentration weight gain, and other issues, testosterone replacement therapy in combination with other treatments may help.



